Which stem cells are used in cirrhosis and fibrosis?
Mesenchymal stem cells (SCs) are used in liver cirrhosis and fibrosis. They can be obtained from blood or adipose tissue. Such stem cell treatment is safe because mesenchymal SCs have low immunogenicity.
More than a thousand clinical studies on the use of mesenchymal SCs in various diseases have been conducted in the world, including more than fifty studies on their use in the treatment of liver diseases. It was found out that stem cells have an anti-inflammatory effect and reduce hepatocyte damage.
Their effectiveness in fibrosis, cirrhosis of the liver and other pathologies of this organ is confirmed by dozens of studies.
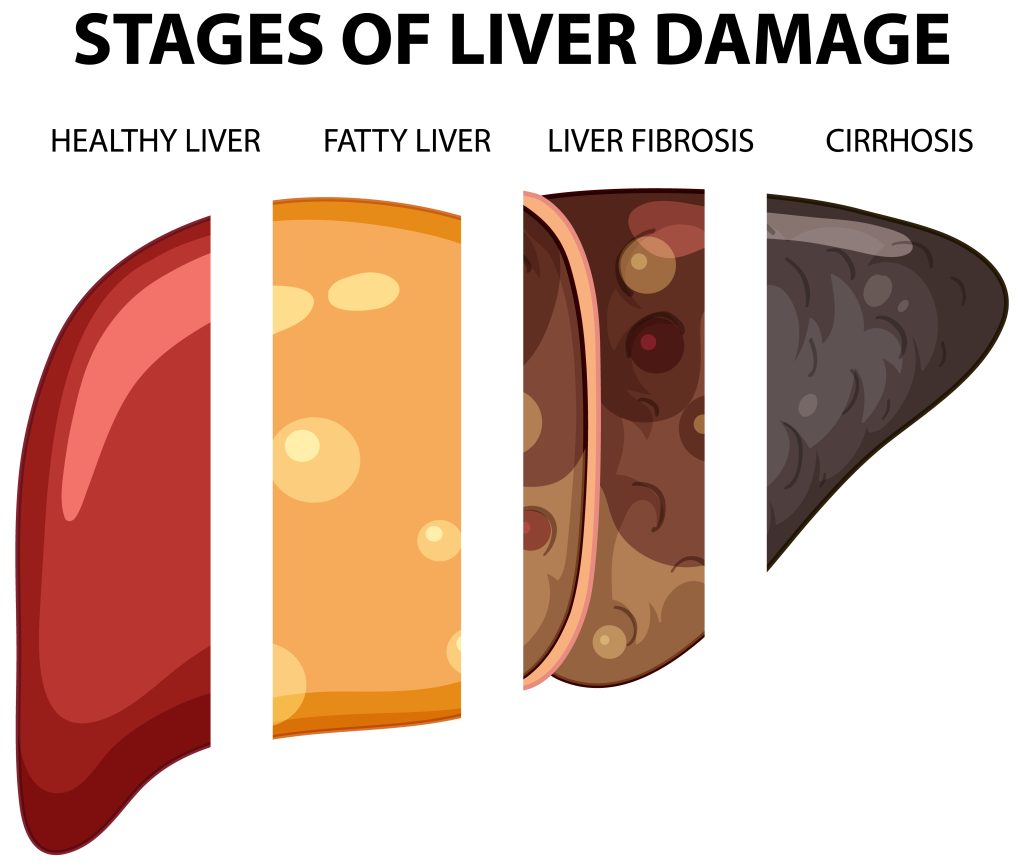
Scientists who used SC from bone marrow concluded that they improve the structure of the liver. The effect was proved with the help of biopsy. Six months after a single injection of stem cells, the area of fibrosis in the samples decreased by 25%, after two injections – by 37%. Other studies have shown improved laboratory parameters and reduced mortality from liver cirrhosis.

How is stem cell treatment for liver cirrhosis and fibrosis?
Currently, the treatment of liver cirrhosis with SC is not considered a standard therapy. The technique is used mainly within the framework of clinical trials. Different clinics use different approaches to stem cell treatment.
When treating cirrhosis and fibrosis, SCs can be obtained from different sources: peripheral and umbilical cord blood, bone marrow, adipose tissue. Both own and donor SCs are used. Stem cells are usually injected intravenously. After injection they migrate to the focus of the lesion, stimulate tissue regeneration and mature into hepatocytes themselves, replacing damaged liver tissue.
As a result of stem cell therapy for cirrhosis and fibrosis, several positive outcomes are observed:
- Symptoms such as fatigue, jaundice, and abdominal discomfort are significantly reduced, improving the patient’s overall comfort and quality of life.
- The patient’s general condition improves, with increased energy levels and a greater ability to engage in daily activities.
- Laboratory parameters, such as liver enzymes and other markers of liver function, often normalize, reflecting better liver health.
- Inflammation within the liver is reduced, helping to slow down the damage caused by cirrhosis.
- The activity of liver fibrosis is decreased, and the risk of complications, such as infections, bleeding, and liver failure, is significantly reduced.
- The progression of pathological changes in the liver slows down, preventing further deterioration and reducing the need for a liver transplant.
The treatment involves different doses, frequencies of administration, and a varying number of injections, depending on the individual case. Regardless of these variations, the therapy has proven to be effective, with results that can last for several months. For sustained benefits, cell therapy can be repeated, stimulating further regeneration and helping to maintain the liver’s functionality. This approach offers hope for those suffering from liver diseases by managing cirrhosis progression and potentially reducing the need for more invasive treatments.
Additional research and prospects for the use of stem cells
Despite encouraging results, the use of stem cells in liver cirrhosis and fibrosis is still under active research. The use of mesenchymal stem cells (SCs) continues to be studied in various clinics around the world, and new studies offer hope for expanding their use. For example, some studies are looking at combining stem cells with other treatments, such as pharmacotherapy or gene therapy, which may lead to a more effective outcome.
Research is also being conducted to improve the methods of delivering stem cells to the affected areas of the liver, such as using nanotechnology. This could improve the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the number of injections needed, making the therapy more affordable and less invasive for patients.
Advantages and safety of stem cell therapy for cirrhosis and fibrosis
- Low immunogenicity: Mesenchymal stem cells have a low level of immune response, which reduces the risk of rejection and complications during use.
- Regenerative ability: Stem cells can migrate to affected areas of the liver and stimulate repair of damaged tissue.
- Anti-inflammatory effect: SCs reduce inflammation, which is important for slowing the progression of cirrhosis and fibrosis.
- Reducing the risk of complications: Therapy helps to reduce symptoms, normalize laboratory parameters and slow down the development of pathological changes.
- Safety: Mesenchymal SCs derived from the patient’s own tissues do not cause serious side effects, which makes the treatment safe.
- Long-term effect: Treatment results can be maintained for several months, and the therapy can be repeated to prolong the effect.
Conclusion
The use of stem cells, especially mesenchymal cells, in the treatment of liver cirrhosis and fibrosis is a promising and safe method that continues to evolve. Multiple clinical studies support the efficacy of this approach, showing improved liver function, reduced inflammation and disease progression. Although stem cell therapy is not yet the standard of care, its use in clinical trials is already yielding encouraging results.
Stem cell therapy offers significant benefits, including tissue regeneration, low immune rejection risk, and long-lasting effects, positioning it as a valuable complement to current liver disease treatments. As technology progresses and methods for delivering stem cells become more refined, this therapy has the potential to evolve into a cost-effective and powerful alternative to conventional approaches for treating cirrhosis and liver fibrosis in the future.





